The compgen command is a very handy tool available in major Linux distributions that can help you find your system aliases, shell built-ins, commands, directories, groups, jobs, users, etc.
In this article, you will learn how to use the compgen command with practical examples.
Tutorial Details
| Description | Compgen |
| Difficulty Level | Low |
| Root or Sudo Privileges | No |
| OS Compatibility | Ubuntu, Manjaro, Fedora, etc. |
| Prerequisites | compgen |
| Internet Required | No |
Listing All Aliases
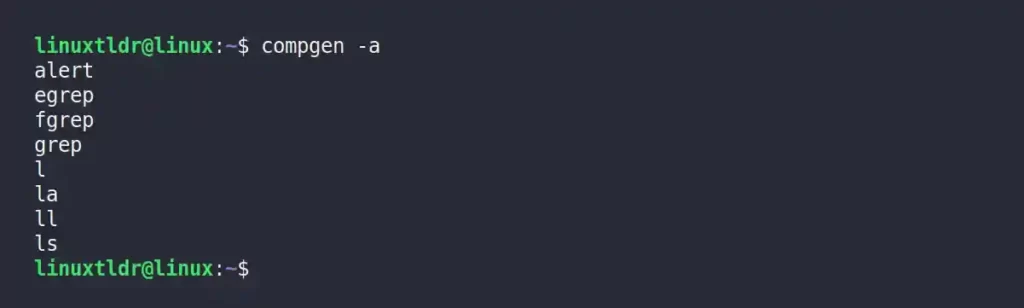
Execute the following command to get the list of all aliases that refer to an existing command.
$ compgen -aOutput:
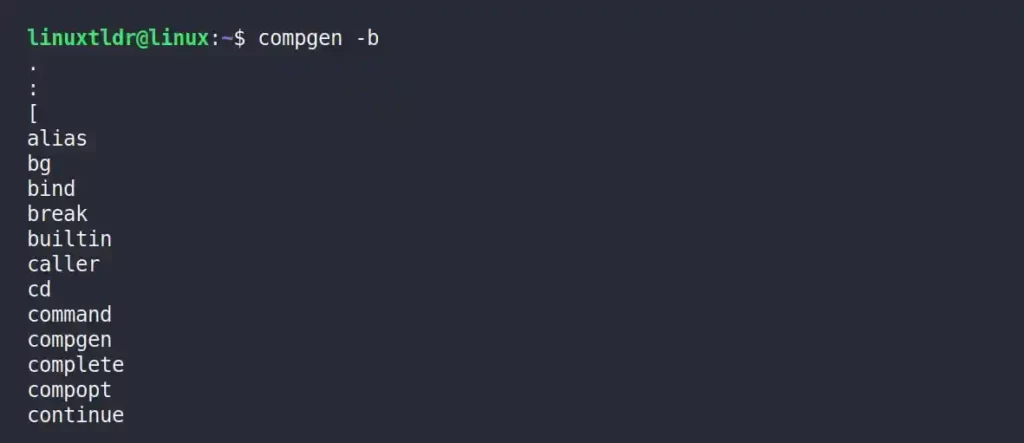
Listing the Names of Shell Built-In
The following command will list the shell’s built-in commands.
$ compgen -bOutput:
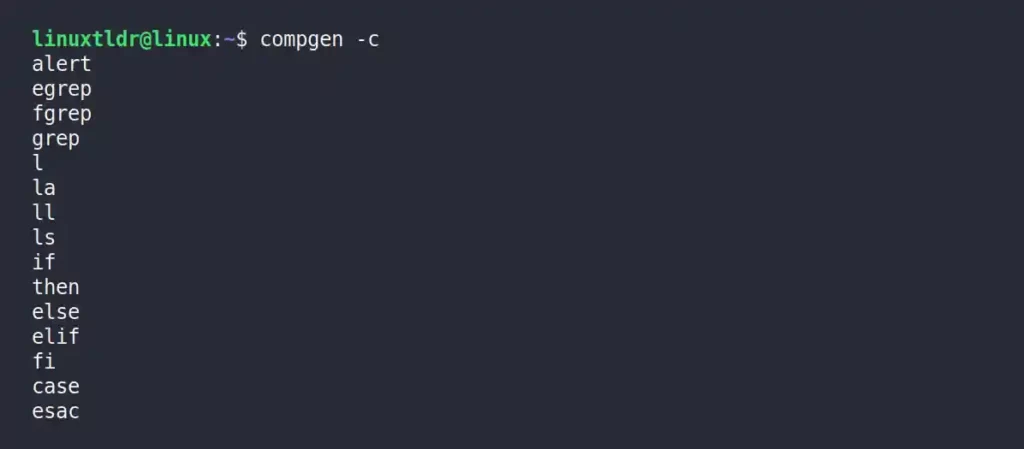
Listing the Names of All Commands
The following command will display a list of all commands that are executable from the command line or can be used in shell scripts.
$ compgen -cOutput:
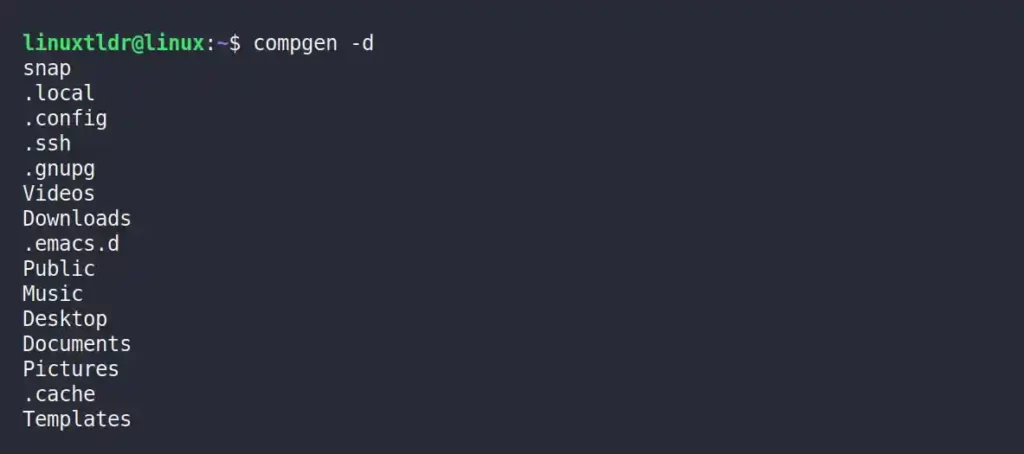
Listing the Names of Directories
It will output all the visible and hidden directories (except files) in your current working directory.
$ compgen -dOutput:
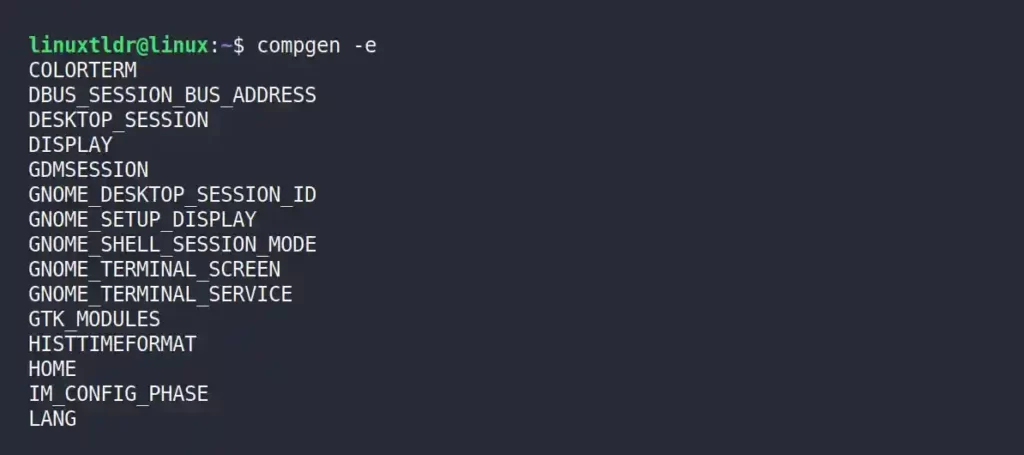
Listing the Names of Exported Shell Variables
The following command will display the list of all shell environment variables for the logged-in user.
$ compgen -eOutput:
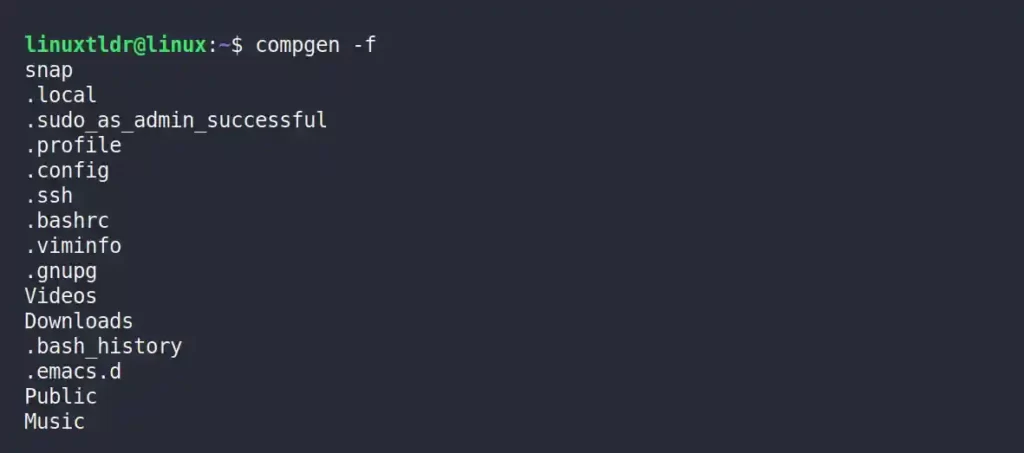
Listing All the Files and Directories
Unlike the “-d” flag, the following command will list all the files and directories in your current working directory.
$ compgen -fOutput:
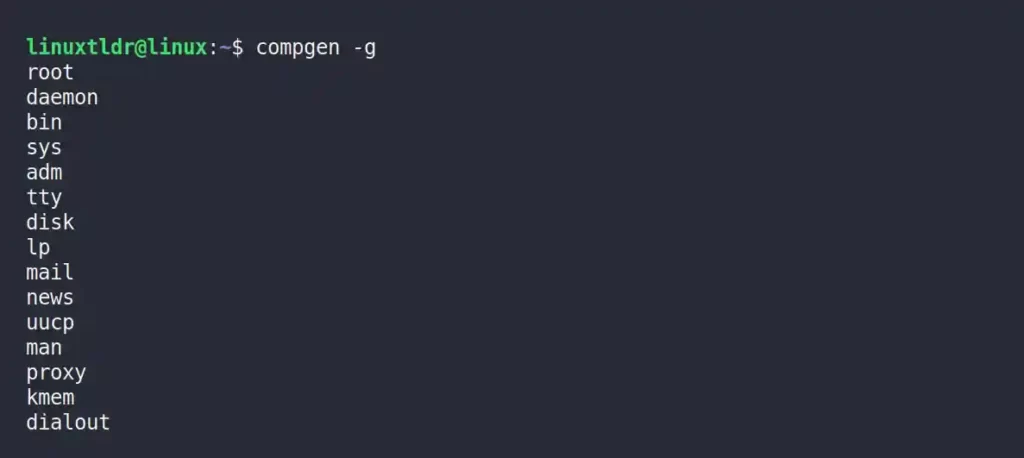
Listing the Names of Groups
The following command will read the “/etc/group” file to give you the list of all groups in your system.
$ compgen -gOutput:
Listing the Names of Jobs
Check all the background jobs or suspended programs using the “Ctrl+z” shortcut key by executing the following command.
$ compgen -jOutput:

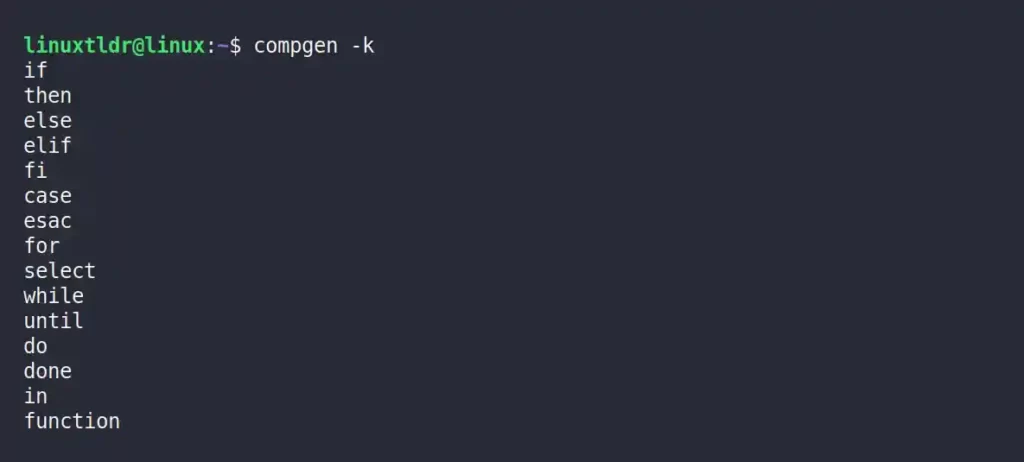
Listing the Names of Shell Reserved Words
The Linux shell reserves a few keywords that you are prohibited from using while creating functions, environment variables, files, or directories.
Execute the following command to get the list of all reserved keywords by shell:
$ compgen -kOutput:
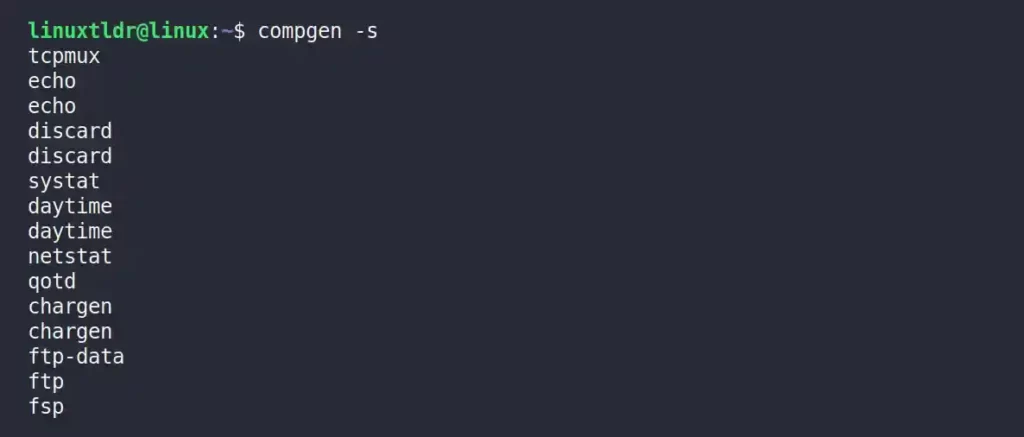
Listing the Names of Service
The following command will display the list of system services that you can manage with the systemctl command.
$ compgen -sOutput:
Listing the Names of Users in Your System
The following command will read the “/etc/passwd” file to give you the list of usernames created by you or by the system services.
$ compgen -uOutput:
That’s all for now. We’ll talk to you in the next article.