Executing the history command without specifying any options will give you a clean record of previously executed commands with their event numbers.
$ history 10Output:
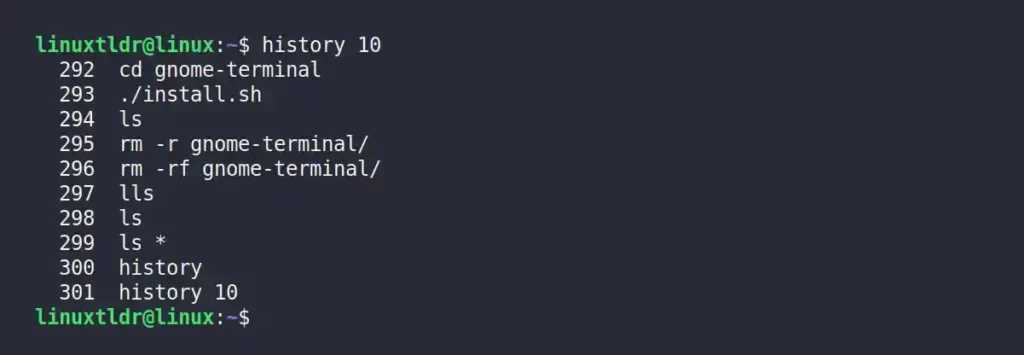
As you can see, it does not display the date and time, so without them, you can’t even manage to filter the records.
In this article, you will learn how to add a date and time to history records, different examples, and how to filter the records based on the date and time.
Tutorial Details
| Description | Display and Filter History Records Based on Date and Time |
| Difficulty Level | Low |
| Root or Sudo Privileges | No |
| OS Compatibility | Ubuntu, Manjaro, Fedora, etc. |
| Prerequisites | history |
| Internet Required | No |
How to Include Date and Time in History Records
You need to modify the shell configuration file, like “~/.bashrc” for Bash shell, with the “HISTTIMEFORMAT” variable, using your choice of text editor, either Vim or Nano, to display the date and time in history records.
$ vim ~/.bashrcOutput:
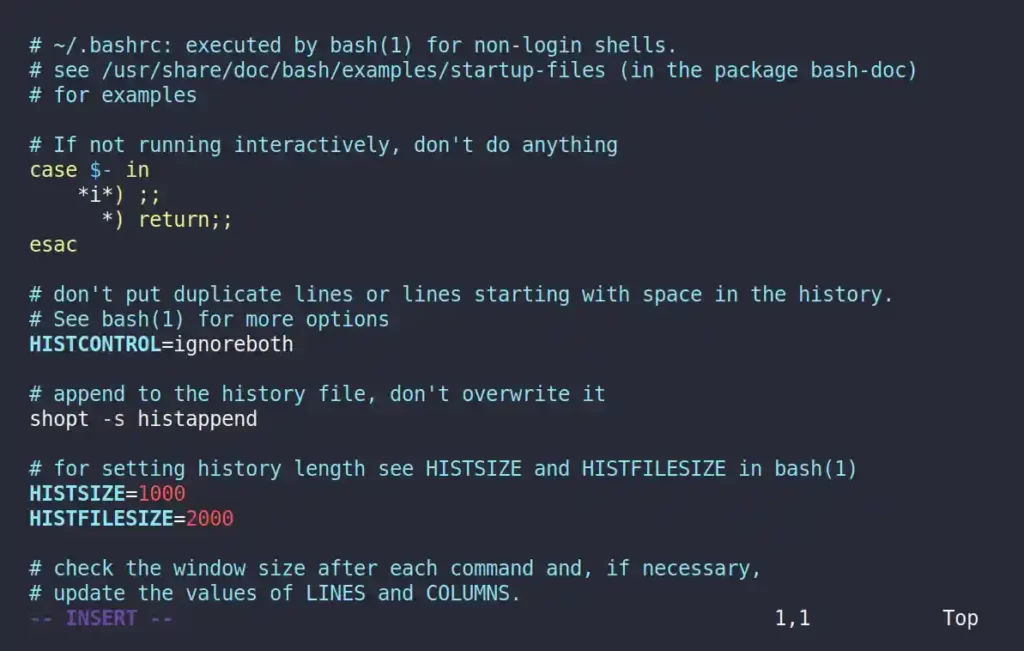
Then add the following line at the end of the configuration file to display the complete date and time in the history records.
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%c "Output:
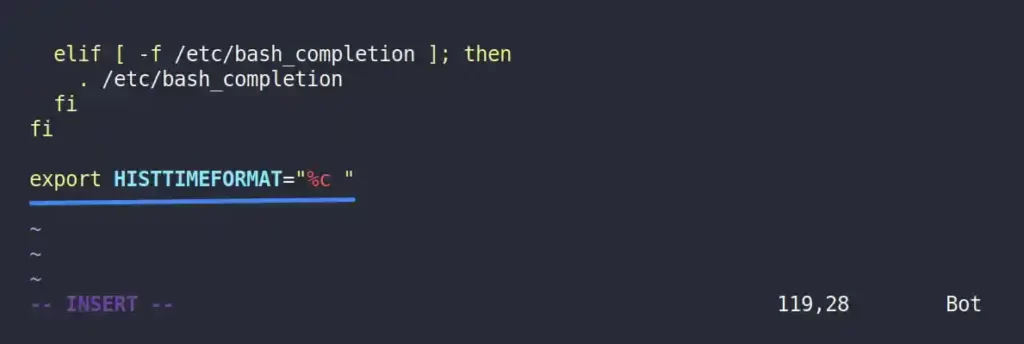
Save and close the file, then reload the shell configuration changes using the source command.
$ source ~/.bashrcOutput:

Finally, run the history command to confirm the new output format.
$ history 5Output:
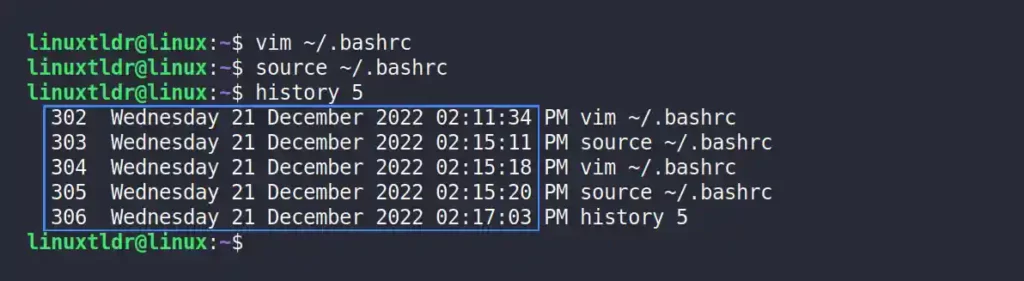
More Examples with Different Formats
Instead of using the predefined date and timestamp “%c” format, you can customize the output with multiple other formats to improve the level of detail in the history records.
The following is a list of all known date and time format codes:
| Codes | Description |
|---|---|
%d | Day |
%m | Month |
%y | Year |
%H | Hour |
%M | Minutes |
%S | Seconds |
%F | Full date (Y-M-D format) |
%T | Time (H:M:S format) |
%c | Complete date and timestamp (D-M-Y H:M:S format) |
The following are a few examples that you can follow to improve your skill in this format’s usage.
Displaying the Date and Time in the History Records
Use the “%F %T => ” code to display the date in “Y-M-D” format and the time in “H:M:S” format, and “ => ” used with spaces before and after to improve readability.
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T => "Output:
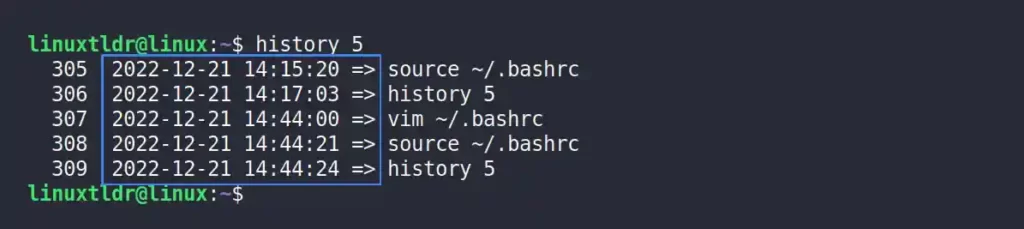
Displaying the Custom Date and Time Format in History Records
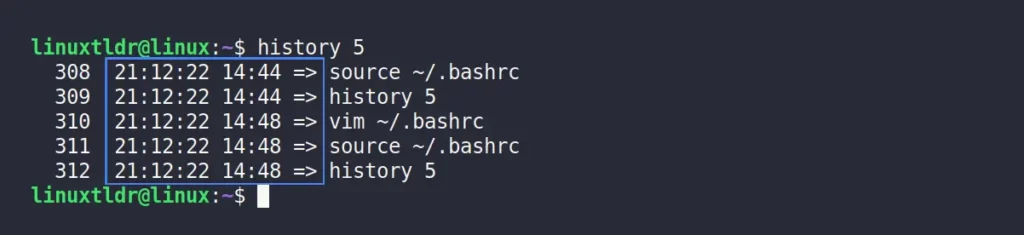
This time, use the “%d:%m:%y” code to display the date in “D:M:Y” and “%H:%M” to display the time in “H:M” format.
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%d:%m:%y %H:%M => "Output:
Displaying the Date and Time in a Fancy Way
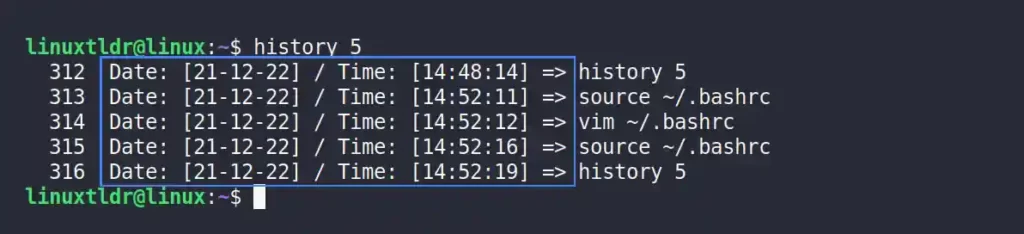
The “Date: [%d-%m-%y]” code will show the date in “Date: [D-M-Y]” format, and “Time: [%T]” will show the time in “Time: [H:M:S]” format.
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="Date: [%d-%m-%y] / Time: [%T] => "Output:
Filtering the History Records Based on Date and Time
Once you include the date and time format codes in the shell configuration file, it will show you that all the commands were executed on the same day. Once you execute the new command on the next day, it will pick the new date and time.
Following are a few examples that are intended to work with “%F %T” format code or something similar that will filter the command history based on different dates and times.
Listing the History Records for a Specific Date
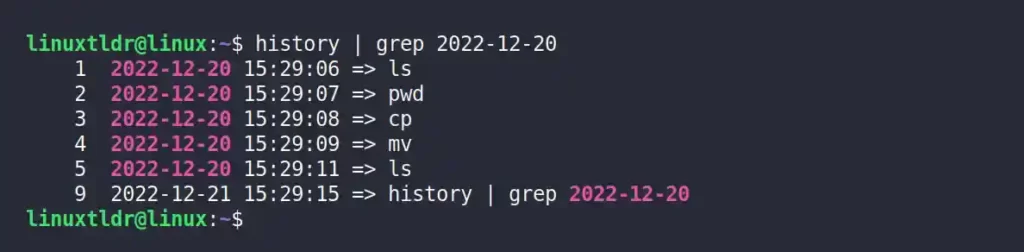
Use the grep with history command to display the list of history records for a specific date.
For example, the following command will display the list of all commands executed on the “2022-12-20” date.
$ history | grep 2022-12-20Output:
Listing the History Records for Multiple Dates
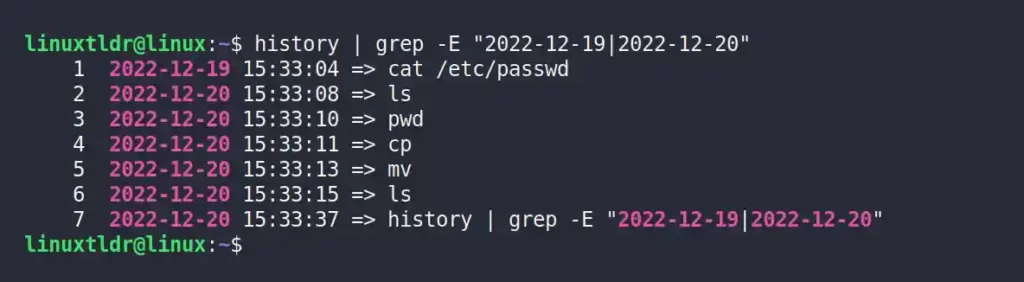
The following command will display the list of all commands executed on the “2022-12-19” and “2022-12-20” dates.
$ history | grep -E "2022-12-19|2022-12-20"Output:
Listing the History Records Based on a Range of Dates
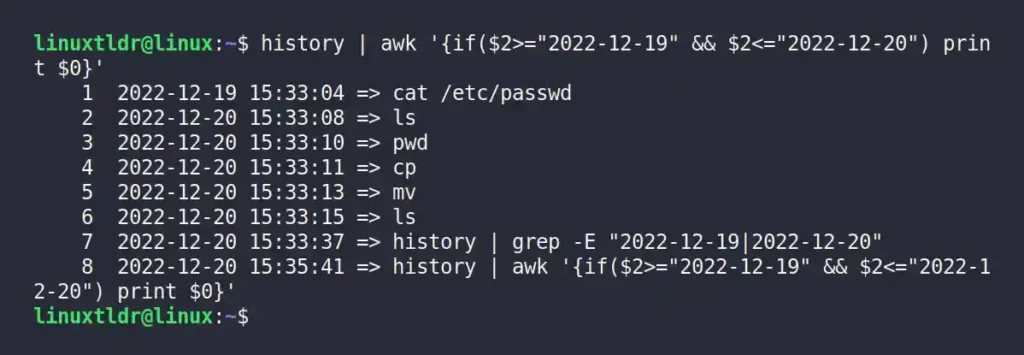
The following command uses the awk command to display the range of commands executed between the “2022-12-19” and “2022-12-20” dates.
$ history | awk '{if($2>="2022-12-19" && $2<="2022-12-20") print $0}'Output:
Listing the History Records Based on a Range of Time for a Specific Date
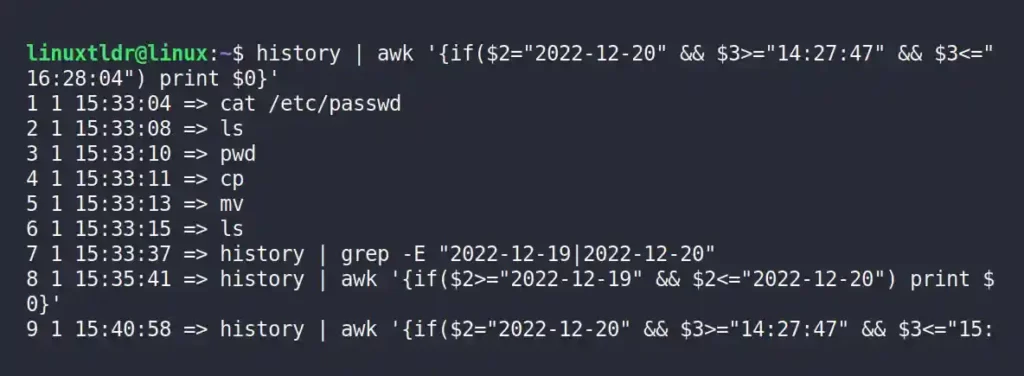
The following command will display the range of commands executed between “14:27:47” and “16:28:04” on “2022-12-20“.
$ history | awk '{if($2="2022-12-20" && $3>="14:27:47" && $3<="16:28:04") print $0}'Output:
Final Tips!
Using date and time in history records will help you a lot while searching for a specific command.
If you want to remove the date and time appearing in the history record, then remove the line added in your shell configuration file.
Lastly, if you have any questions or queries regarding this topic, feel free to ask them in the comment section.