A Linux server is operated by multiple users who can login and logout at any given time without any restriction (of course, they should have the proper privileges).
In an occasion like a data breach, you might want to track user activity to investigate the incident, and as a sysadmin, you might want to know who, when, and from where logged into the target machine.
In this case, you can use the last command, a fantastic built-in Linux utility.
Tutorial Details
| Description | Show a Log of the User’s Login History |
| Difficulty Level | Low |
| Root or Sudo Privileges | No |
| OS Compatibility | Ubuntu, Manjaro, Fedora, etc. |
| Prerequisites | last |
| Internet Required | No |
What is the Last Command in Linux?
The last command is a tool that sysadmins often use to keep track of user sessions on the server. It can list information about users, such as their usernames, when they log in and out of the system, where they log in from, etc.
This information is pulled from the “/var/log/wtmp” file, which is always modified in the event of a user’s login and logout. You can check out our dedicated article on this topic.
This article will focus mostly on how to use the last command and its different options.
Usage of the Last Command
The last command takes two arguments: one is the option, and the other is the username or TTY (all are optional).
$ last [OPTION] [USERNAME/TTY]If you run the last command without any arguments, the following screen will appear:
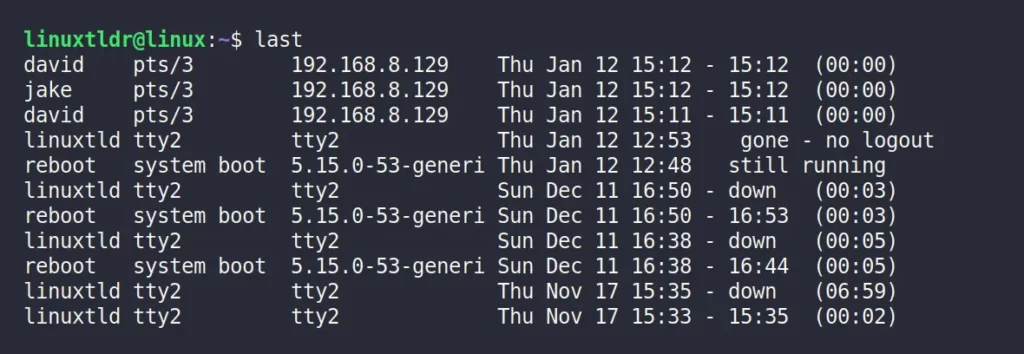
Note that this record is listed in reverse chronological order; the first will be the latest record; in this case, the “david” user has recently logged in to the system.
The following is an explanation of each field in the output:
- The username, note that in the event of a system reboot or shutdown, the “
last” shows special users “reboot” and “shutdown“. - The tty user used to start the login process. “
pts/*” means via SSH, “tty*” means via terminal, and “0:” means via the desktop environment. - The host name or the IP address from which the user logged in.
- The login and logout times.
- The duration of the user session; if the user fails to logout, the message “
no logout” appears. If the user is still active, it will show “still running” in place of duration.
Now, let’s move on to the next section.
How to Check a Specific User’s Login History
If you know all the user’s login names on the target machine, then you can use that to filter out the result for a particular user.
$ last davidOutput:
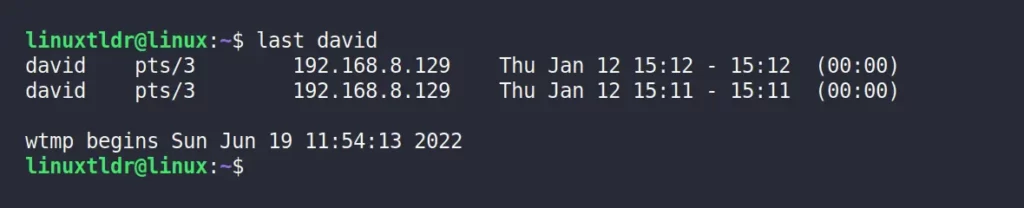
From the above picture, it appears that “david” has initiated the login process multiple times on the “Jan 12” date.
How to Check Login History Based on TTY
Unlike the previous command, you can investigate the user based on TTY; for example, you can specify “pts/*” to check the login attempts held on the target machine via SSH.
$ last pts/3Output:
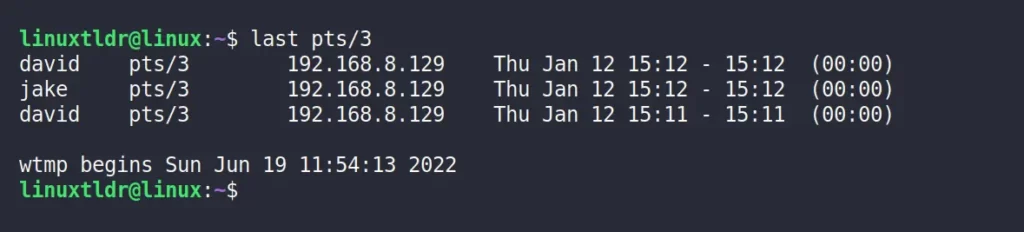
From the above picture, it appears that the “david” and “jake” users logged in to the target machine on the “Jan 12” date via SSH.
Now, let’s move on to the next section to check all the options offered by this command.
Last Command Options
The last command supports a variety of options that can limit the entries in the output, display login history for a specific or range of dates, hide/show columns, etc.
Limit the Entries to N Number in the Output
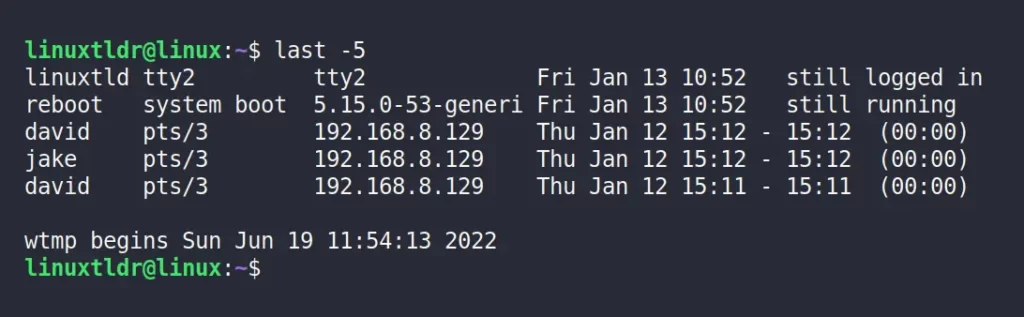
The “-N” option, where “N” refers to any positive integer, is used to specify the number of lines (or entries) to display in the output.
$ last -5The above command will return the latest five entries in the output.
Display the Login History For Today and Yesterday
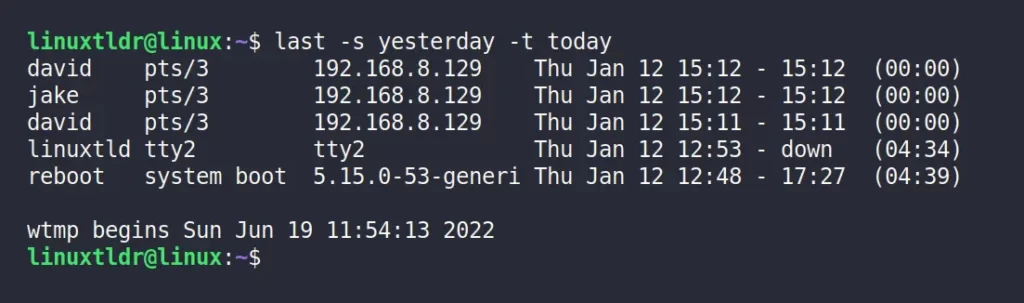
The following command will display the login history for today and yesterday, whereas the “-s” flag represents “since” and the “-t” flag represents “until“.
$ last -s yesterday -t todayOutput:
Display the Login History For a Specific Date
The “-p” flag can be used to show the log of login history for a particular date specified in “YYYY-MM-DD” format.
$ last -p 2022-11-18 Output:
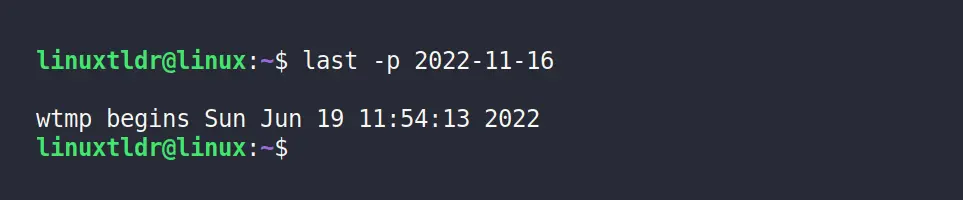
Display the Login History For Range of Dates
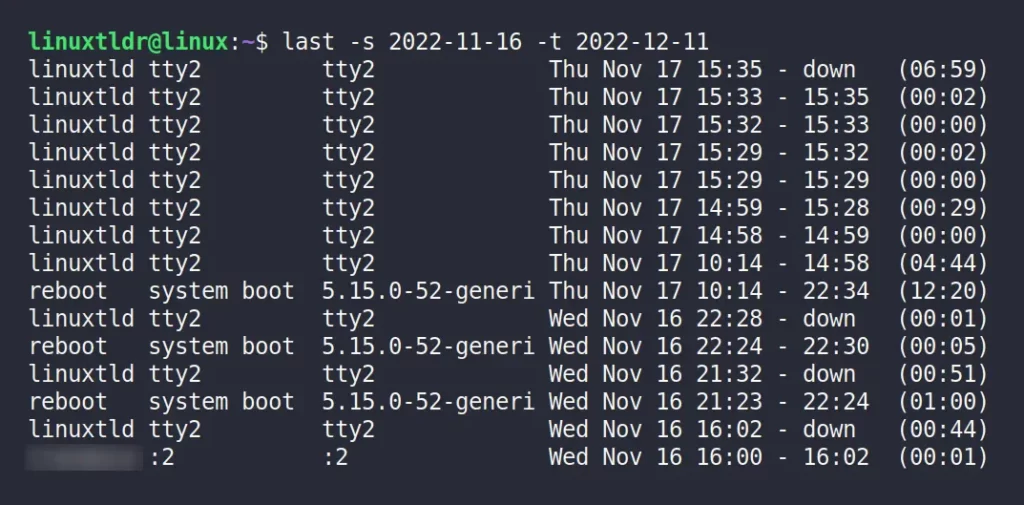
The following command will display the login history from “2022-11-16” to “2022-12-11“.
$ last -s 2022-11-16 -t 2022-12-11Output:
Display the Login History for the Last Few Days
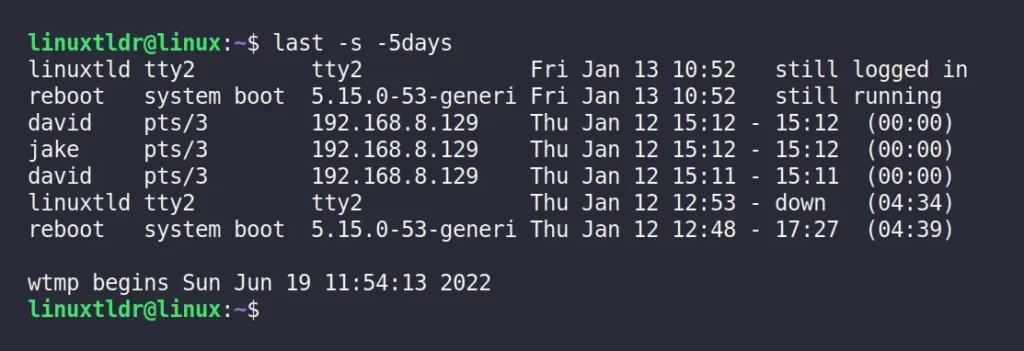
The following command will display the login history for the last five days.
$ last -s -5daysOutput:
Display the Reboot History
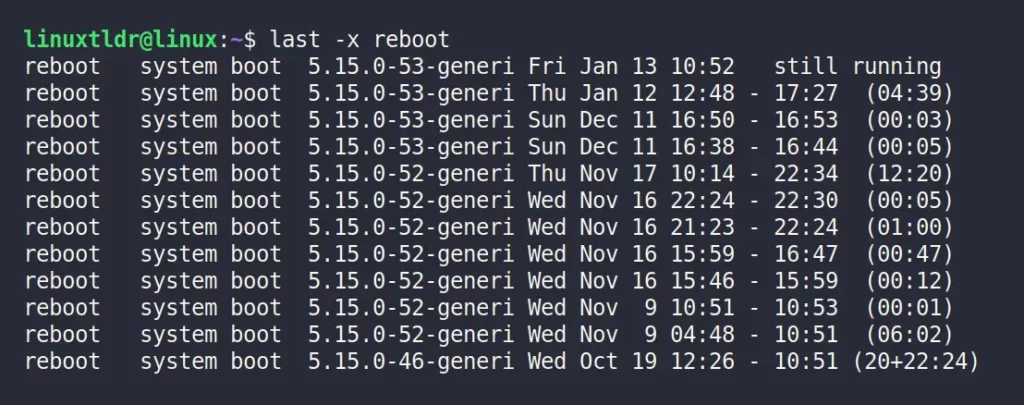
Each time a user reboots the system, a new entry is written in the file with a special “reboot” username that can be used to show a log of all reboots since the log file was created.
The following command will show all the entries with system reboots and run levels changes using the “-x” flag.
$ last -x rebootOutput:
Display the Shutdown History
Similar to the previous command, whenever users shutdown the system, a new entry is written in the file with the special “shutdown” username.
$ last -x shutdownOutput:
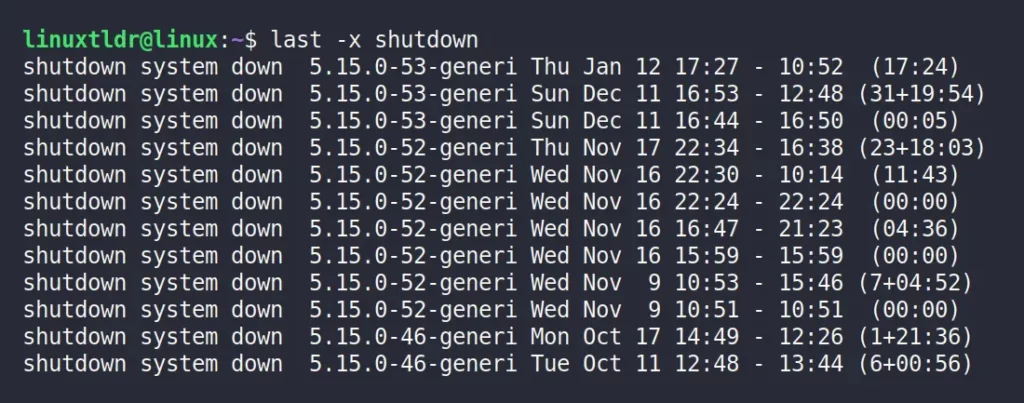
Display the Hostname Field in the Last Column
The “-a” flag will move the hostname field to the last column so that the result doesn’t get cut off.
$ last -aOutput:
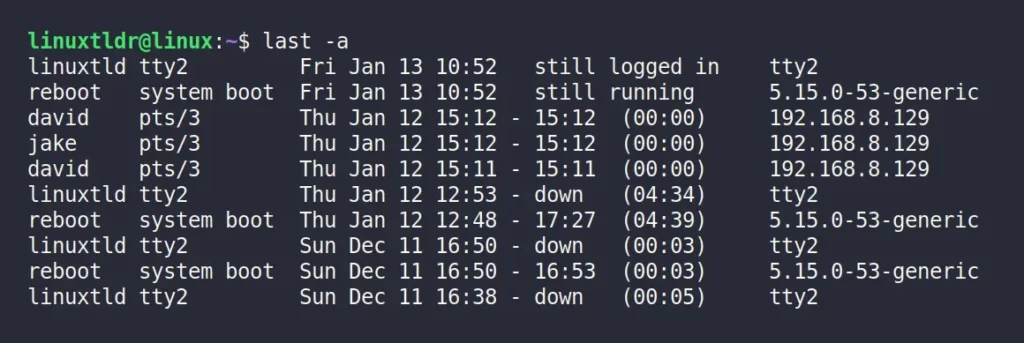
Hide the Hostname Field From the Output
The “-R” flag will remove the hostname field from the output.
$ last -ROutput:
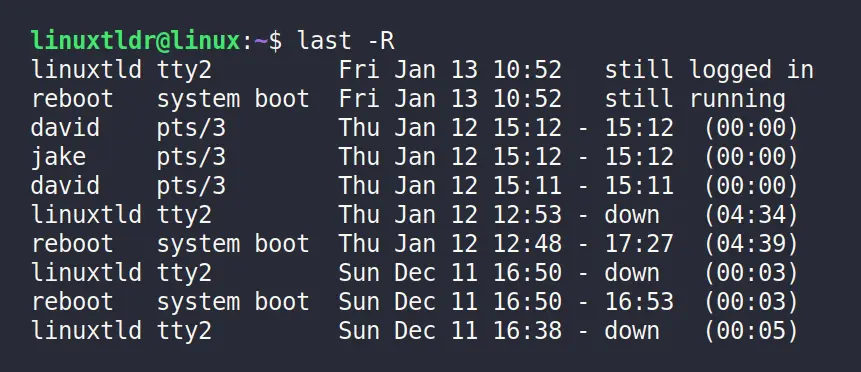
Display the Full Login and Logout Timestamp
The “-F” flag will display the timestamp entries for login and logout in full format.
$ last -FOutput:
And here comes the end of all examples.
Bonus Tip! How to Check a User’s Failed Login Attempts
Isn’t it good to look up a user’s login and logout history? But while investigating the user’s login history, you must also consider the failed login attempts held on the target machine.
The last command does not display the failed login attempts by users; for this, you have to use another command-line tool known as the lastb command.
The following command will show a log of all the failed login attempts made by the users on the target machine.
$ sudo lastbOutput:
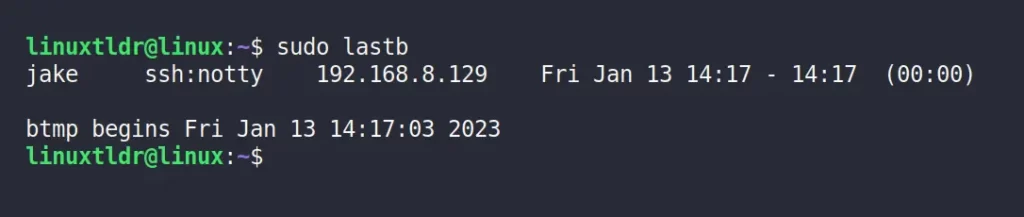
The above output shows that the “jake” user tried to access the target machine via SSH with the wrong authentication information.
Let’s finish this article here; I think you can dig further by yourself.
If you have any questions or queries related to this topic, then feel free to ask them in the comment section.
Till then, peace!