Are you also facing the “pkg-config script could not be found” or “configure: error: pkg-config is required” error while compiling your favorite program? Then just run one of the following commands based on your Linux distribution, and the problem will be resolved.
# On Debian, Ubuntu, Kali Linux, Linux Mint, Zorin OS, Pop!_OS, etc.
$ sudo apt install pkg-config
# On Red Hat, Fedora, CentOS, Rocky Linux, AlmaLinux, etc.
$ sudo dnf install pkgconfig
# On Arch Linux, Manjaro, BlackArch, Garuda, etc.
$ sudo pacman -S pkgconf
# For macOS
$ brew install pkg-configInterested in knowing more about this package? Then, let’s start.
What is pkg-config in Linux?
pkg-config is a helper tool that is used to provide the correct path of header files or libraries to the compiler option during the compilation of an application or program.
It often happens that the path of header files or libraries varies for different systems; instead of hard-coding them, pkg-config helps determine the proper paths to header files and code to link them to your software project.
It’s free, open-source, and originally released for Linux and other UNIX-like systems, but later ported to Windows and macOS. The program code has been rewritten multiple times, with the first implementation by James Henstridge and the current one maintained by Tollef Fog Heen.
Let’s now see how pkg-config can help us find the correct path to pass to the compiler.
Usage of pkg-config command
pkg-config helps during the compilation of applications by providing paths to the installed header files and libraries. To learn its usage, you must first find out the list of available packages on your system using this command:
$ pkg-config --list-allOutput:
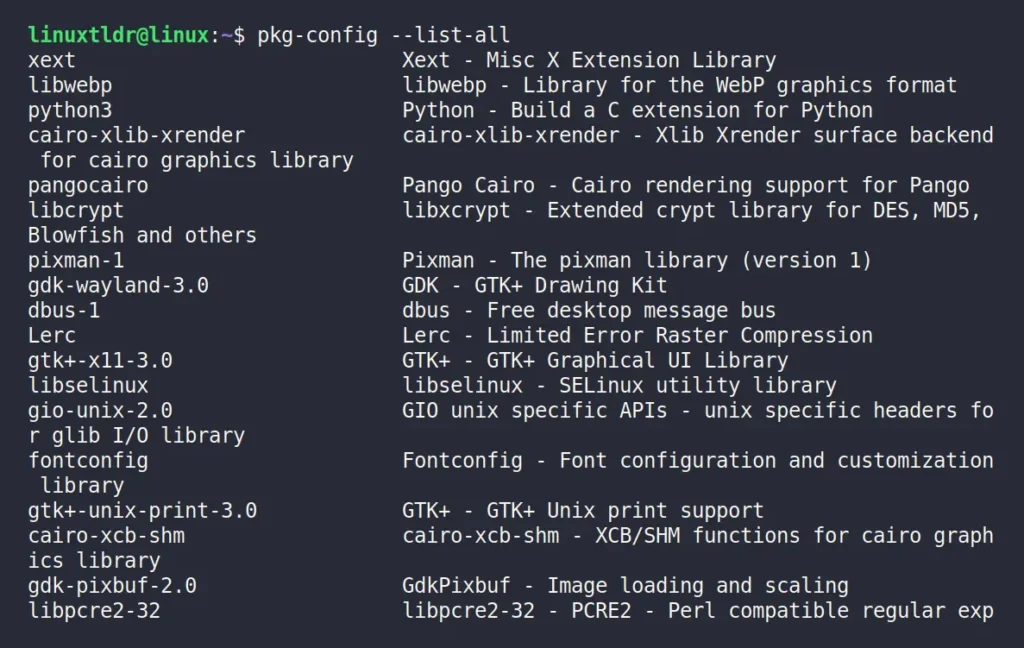
Once you have selected the package name, you mainly use the following two options:
- “–cflags“: It will provide the path for the “-I” (include) compiler option, typically for header files.
- “–libs“: It will return the path for the “-L” (libs) compiler option, which is often used to link compiled libraries to new code.
Let’s say you want to find the compiler option for the “python3” package, you can run:
$ pkg-config --libs --cflags python3Output:
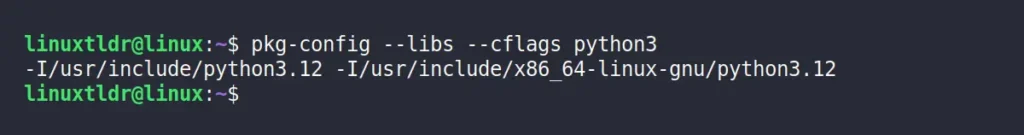
In this scenario, there is only one path for each “include” and “libs” compiler option. However, certain packages, like “gtk+-3.0” may offer multiple paths.
$ pkg-config --libs --cflags gtk+-3.0Output:
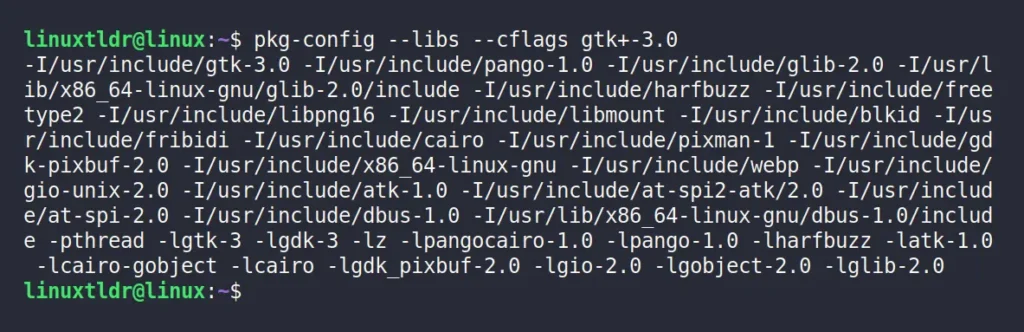
These outputs can be used for program compilation. You can either copy-paste it or assign it to a custom environment variable. For example, exporting the output of the pkg-config command to the compiler via environment variables would look like this:
$ export COMPILER_PATHS=$(pkg-config --libs --cflags LIBRARYNAME)Afterward, you can use this environment variable to compile your program, like below:
$ COMPILER -c MYPROGRAM ${COMPILER_PATHS} If you’re not a programmer and aren’t involved in compilation, you might wonder why this matters. However, if you do end up involved in compiling other programs via source code, the “configure” file you use to set up the environment might include pkg-config for providing paths. In that case, pkg-config must be installed on your system, or you might encounter the error mentioned in the article introduction.
I hope you understood the concept of pkg-config—what it is, when to use it, and why you should care. If you have further questions, feel free to ask them in the comments.
Till then, peace!