Last night, Fedora unveiled its highly anticipated release, Fedora 40 bringing GNOME 46 desktop and upgraded apps, the new KDE Plasma 6.0 desktop is also available, the Linux 6.8 kernel is powering this beast along with GCC 14 and Mesa 24.0 graphics drivers, and a bunch of software package updates like LLVM 18 along with various exciting features.
Unfortunately, we have not written any dedicated articles on the features offered in Fedora 40 (which is out of the scope of this site), but you can check out this well-written blog or YouTube video.
In this article, you will learn how to upgrade from Fedora 39 to 40 using your terminal or desktop environment in a matter of seconds.
Tutorial Details
| Description | Upgrading from Fedora 39 to 40 using Terminal or DE |
| Difficulty Level | Moderate |
| Root or Sudo Privileges | Yes |
| OS Compatibility | Fedora 39 |
| Prerequisites | dnf |
| Internet Required | Yes |
A Note for Readers
Now, before you impatiently launch your terminal and execute the following commands, I just want to notify you of a few things to avoid any system crashes or data loss.
- Execute the following command only in Fedora 39 (stable).
- If you are already using Fedora 40 beta, then simply execute the “
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf upgrade” command. - If you are using the two-step older version of Fedora 40, such as Fedora 37 or 38, then avoid using the step to directly upgrade to Fedora 40 (unless you are a deviant).
- In this situation, you can go in order to upgrade your system, like if you are using Fedora 37, then first upgrade to 38, then 39, and then 40, or you can directly perform a fresh installation.
- And also, make sure to take a backup of your system (or at least your files) before performing any system-level task like upgrading (just do it if you’re a newbie).
Keeping all that in mind, let’s move on to the required steps to upgrade Fedora 39 to Fedora 40 from your command-line or desktop environment.
Upgrading from Fedora 39 to 40 in Terminal (CLI)
1. First, open your terminal and upgrade your pending updates using the following command:
$ sudo dnf upgrade --refreshThe above command will upgrade all the packages to their latest version, including those essential for supporting Fedora 40.
2. (Optional) Remove the residual packages, libraries, or dependencies that are no longer required by any other package, thereby indirectly freeing up some storage space.
$ sudo dnf autoremove3. Install the DNF upgrade plugin package that is required in the upgrade process.
$ sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade4. Execute the following command to download all the required packages for Fedora 40.
$ sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=40Note that if you have installed a bunch of packages from the source code, then you need to ensure that they do not create any issues. For that, use the “--allowerasing” flag with the above command to allow the removal of conflicting packages to resolve dependencies.
5. Once the above process is complete, execute the following command to start the upgrading process:
$ sudo dnf system-upgrade rebootNote that the download size will be in GB and might take a good amount of time. So, you have to wait until the upgrade process is completely done (I recommend you not perform any task at the given time).
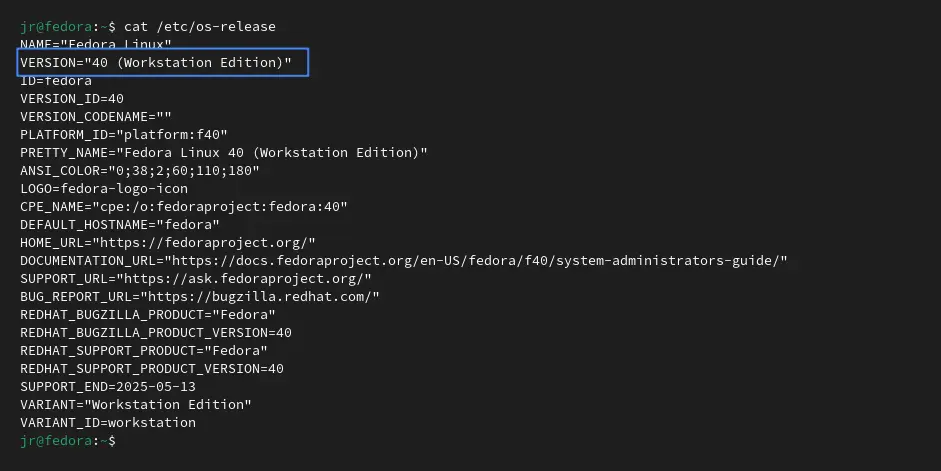
Once the installation process is done and your system is upgraded, you can check your current Fedora version by executing the following command:
$ cat /etc/os-releaseOutput:
Upgrading from Fedora 39 to 40 via DE (GUI)
Of course, this article will be incomplete without showing you the update process in your desktop environment. So, for that, you can simply perform the following steps:
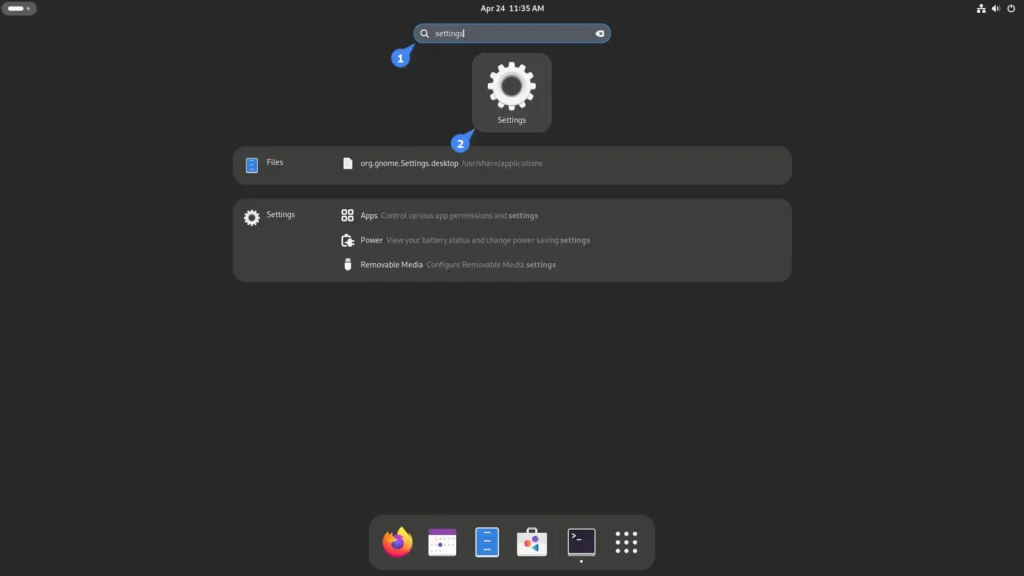
1. Open “Settings” by searching for them or from your notification area.
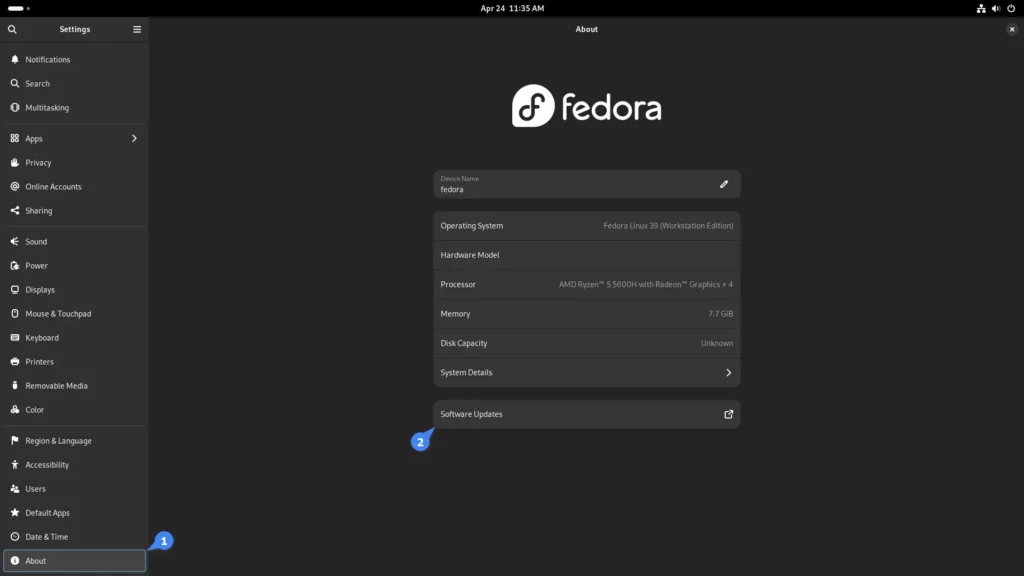
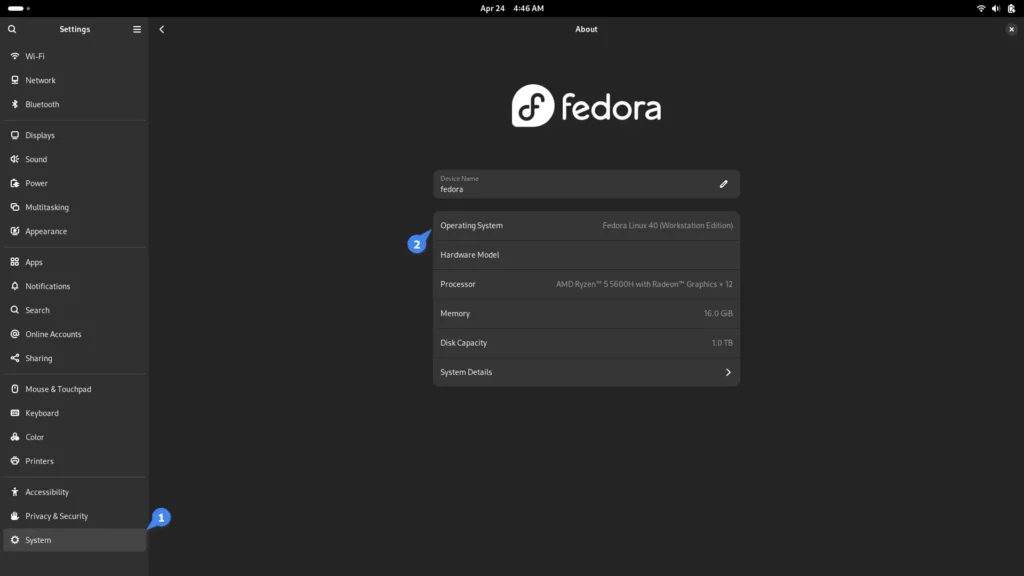
2. Navigate to “About” -> “Software Updates” as shown.
3. Now, if your system is eligible for the update, you will see the following window: You just have to click on the “Download” button to start the upgrade process.
sudo dnf update && sudo dnf upgrade” command, then re-check this section.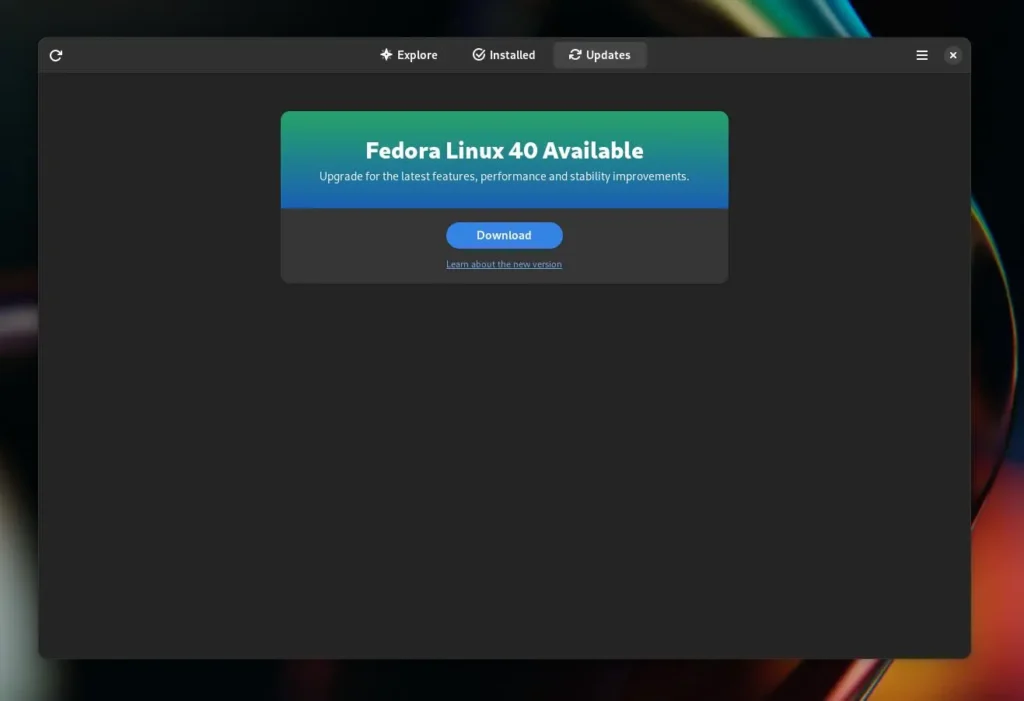
After the installation is complete, you can navigate to “Settings” -> “About” and check your current version next to “OS Name“, as shown.
Post Upgrade Tips (Optional)
Once the upgrade process is complete, you are ready to use your Fedora system as usual. However, there will be some temporary files and cached data associated with the system upgrade — specifically, the downloaded packages and files used during the upgrade process.
To remove them, just execute this command:
$ sudo dnf system-upgrade cleanThis helps free up disk space by getting rid of unnecessary files, ensuring a cleaner and more efficient system after an upgrade.
While removing unnecessary packages, there could be broken symbolic links (or symlinks) pointing to deleted files that might be removed during storage cleanup.
To get rid of broken symbolic links, just execute this command:
$ sudo find /usr -type l -xtype l -delete
#OR
$ sudo symlinks -r /usr | grep dangling #It will list them for you to manually review before deletion.Wrap Up
I already upgraded my system to Fedora 40, and I’m having a great experience. You can also share your experience with this latest release and tell me what you really liked about this version of Fedora.
If you have any questions or queries related to this topic, then feel free to ask for help in the comment section.
Till then, peace!



Hi linuxtldr.com administrator, Thanks for the well written post!
Just upgraded it, and as always, I’m having a great experience with this Fedora version.