The Linux shell (specifically, “Bash“) takes each executed command as an event and saves the command in the “.bash_history” file located in the user’s home directory.
Now, there are two ways to view the history record of a user’s executed command: one using the history command, and the other by reading the “~/.bash_history” file using the cat command.
In this article, you will learn how to view, backup, and restore the Linux command history on a Linux system, so stick with it till the end to learn everything.
Tutorial Details
| Description | Backup and Restore User’s Command History |
| Difficulty Level | Low |
| Root or Sudo Privileges | No |
| OS Compatibility | Ubuntu, Manjaro, Fedora, etc. |
| Prerequisites | history |
| Internet Required | No |
How to View Linux Command History
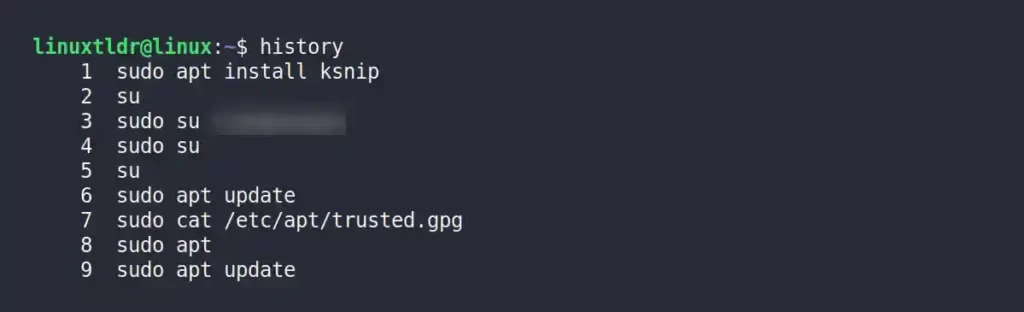
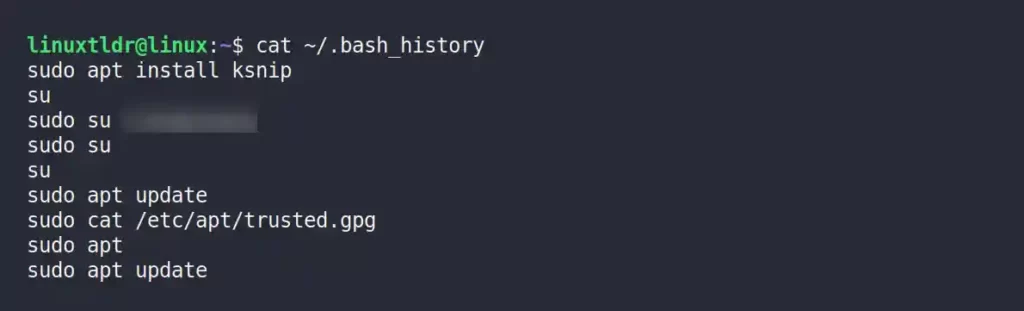
All Linux distributions ship with an amazing tool named “history” that gives you many features and functionality to interact with “~/.bash_history” file, including reading the user command history.
$ historyOutput:
Alternatively, you can read your “~/.bash_history” file using the “cat” command.
$ cat ~/.bash_history
#OR
$ cat $HOME/.bash_historyOutput:
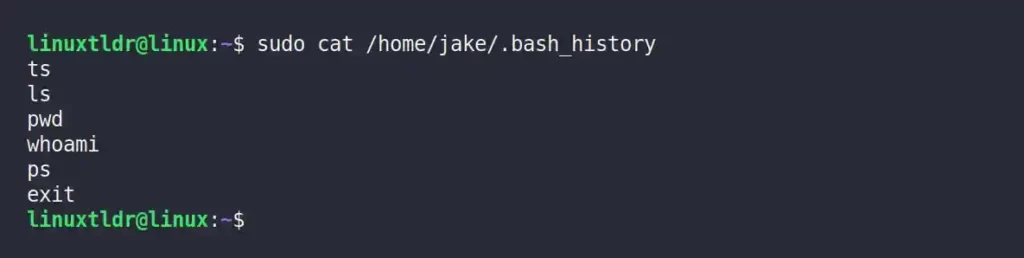
If you want to see another user’s command history, you need to give the location of their “.bash_history” file.
$ cat /home/jake/.bash_historyThe above command will output the user “jake” command history.
Usually, when you execute the history command or view the user command history using the cat command, you will get a list of all user executed commands in the terminal.
Although you might not be interested in a complete list, you can use the grep command to output only a specific user executed command.
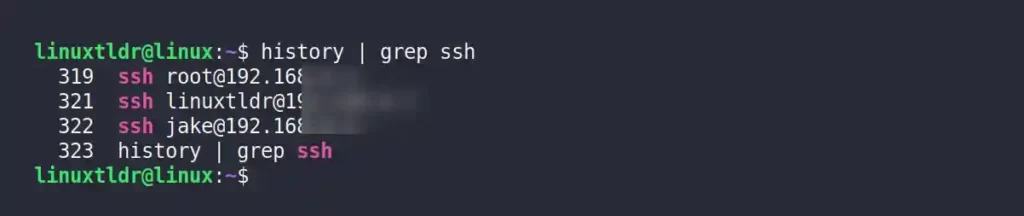
For example, the following two commands will only list the current user’s SSH-related executed commands from the history file:
$ history | grep ssh
#OR
$ cat ~/.bash_history | grep sshOutput:
How to Backup Linux Command History
Now, as you understood, that “~/.bash_history” file keeps the record of user executed commands in the Linux terminal.
So, you can backup this file for the current user or a different user, including all or a specific command.
Backup Current User Command History
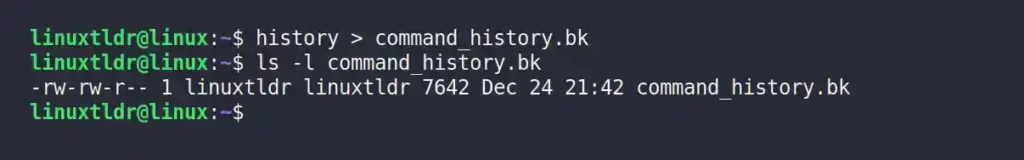
To backup your existing command history record, you can use the history command or “~/.bash_history” file to redirect their output to a different file using the “>” or “>>” redirection symbol.
$ history > command_history.bk
#OR
$ cat ~/.bash_history > command_history.bkOutput:
Backup Another User’s Command History
Like the previous command, you can backup another user’s command history record; however, the history command will not work in this situation as it only reads the current user’s history file.
Still, you can backup another user’s command history by using the cat command with the “>” or “>>” redirection symbol, as shown.
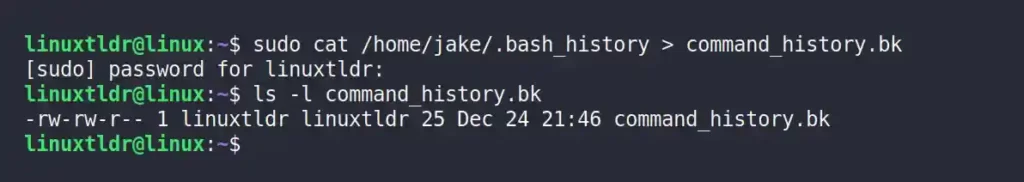
$ sudo cat /home/jake/.bash_history > command_history.bkOutput:
Backup Specific Executed Command History
As we discussed earlier, you are not always going to require the complete list of the user’s command history, so you can pull the specific executed command from the history file for the user.
The following command will backup the current user’s SSH-related executed commands.
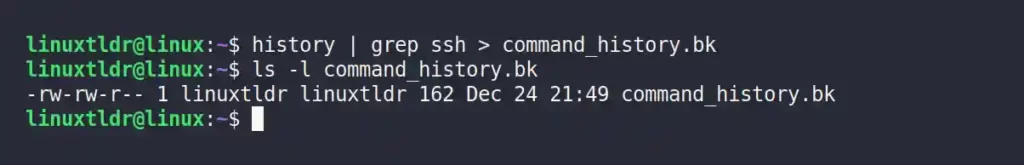
$ history | grep ssh > command_history.bk
#OR
$ cat ~/.bash_history | grep ssh > command_history.bkOutput:
Alternatively, use the following command to backup another user specific executed command.
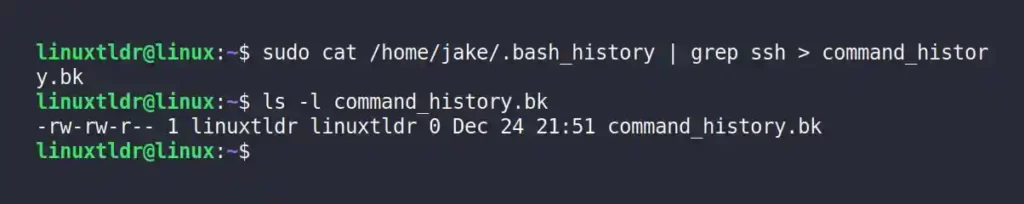
$ sudo cat /home/jake/.bash_history | grep ssh > command_history.bkOutput:
How to Restore Linux Command History
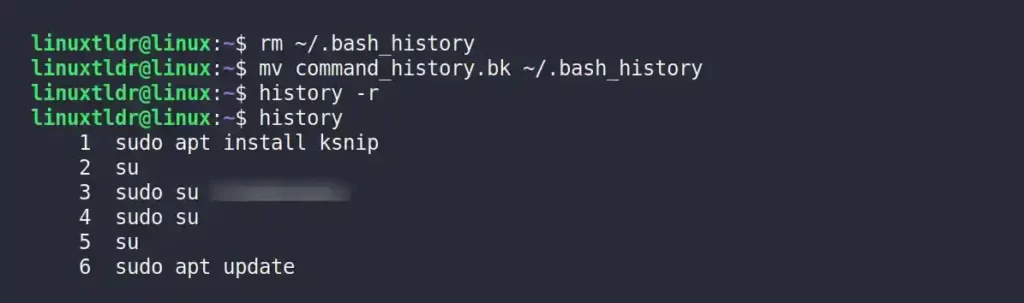
To bring back the user command history, first make a copy of your existing history file using one of the methods above. Then, use the following command to delete your existing history file:
$ rm ~/.bash_history
#OR
$ rm $HOME/.bash_history After that, restore the backed up user command history using the following command:
$ mv command_history.bk ~/.bash_history
#OR
$ mv command_history.bk $HOME/.bash_historyLast, reload the history file and run the following commands to make sure everything was done right:
$ history -r
$ historyOutput:
Final Tip!
That’s all it takes to backup and restore the current or another user’s history record of all or specific commands.
If you want more articles related to this topic, then let us know in the comment section.
Till then, peace!